Topline
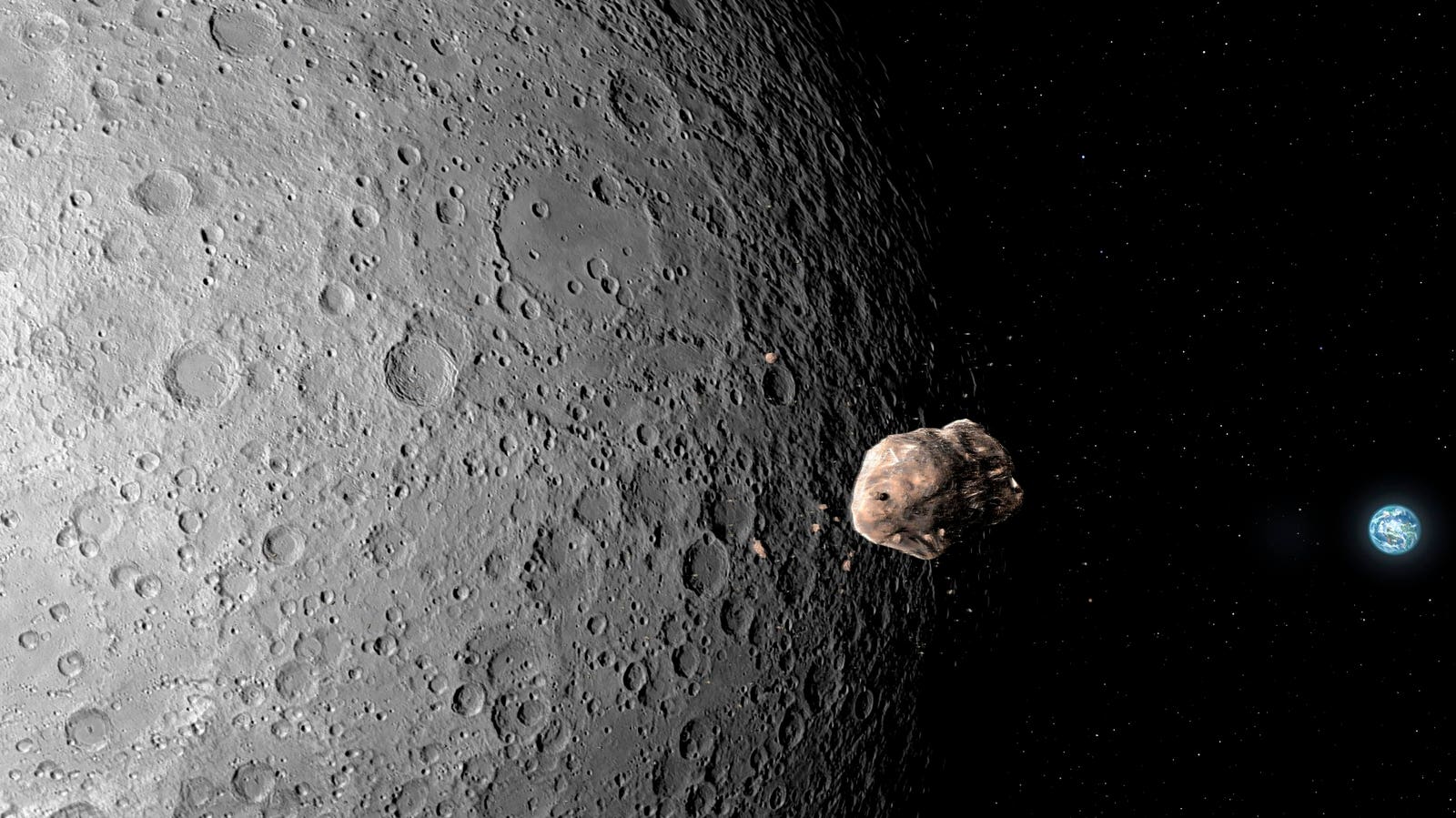
A potential asteroid strike on the moon calculated by NASA could also pose a significant risk to satellites orbiting Earth, according to new research. Scheduled for a possible collision on December 22, 2032, asteroid 2024 YR4’s diameter is equivalent to a 10-story building and would cause a new crater on the moon, ejecting material into space that could threaten the entire satellite fleet orbiting Earth. It could also cause a brief but spectacular meteor shower visible from Earth.
Asteroid 2024 YR4 is 174-220 feet (53-67 meters) in diameter and could impact the moon on December … More
Key Facts
Dubbed a “city killer” when it was initially thought to be heading towards Earth, asteroid 2024 YR4 is 174-220 feet (53-67 meters) in diameter and could impact the moon on December 22, 2032. In that scenario, it would release energy equivalent to 6.5 megatons of TNT, forming a crater roughly one kilometer in diameter, according to a new paper published on June 12 on the preprint platform arXiv.org and submitted to the journals of the American Astronomical Society.
According to the authors at The University of Western Ontario and Athabasca University in Canada, up to 100 million kilograms of lunar material could be blasted into space, with debris potentially escaping the moon’s gravity and heading toward Earth.
Satellites in low Earth orbit — which accounts for about 90% of the global fleet — will be particularly at risk, with hundreds or even thousands of minor impacts across fleets like SpaceX’s Starlink broadband internet constellation. That would happen within a few days of YR4 striking the moon.
Tiny meteoroids are constantly striking satellites, and with ejecta from YR4’s impact measuring only 0.1-10 mm in size, satellites wouldn’t suffer catastrophic damage. However, the huge increase in tiny meteoroids could be equivalent to a decade’s worth, rapidly aging the entire satellite fleet.
Debris could linger in Earth’s orbit for months to years, creating ongoing threats to long-duration missions, such as the James Webb Space Telescope. However, its current position at L2 — a million miles from Earth — minimizes that danger.
While ejecta from a lunar asteroid strike could be damaging to satellites, it would burn up in Earth’s atmosphere, so it won’t directly threaten Earth. However, it may create a brief but spectacular meteor shower.
Chances Of A Lunar Impact
There is currently a 4.3% chance of YR4 striking the moon, according to calculations based on observations by the James Webb Space Telescope in May, according to a post from NASA. That’s an increase from 3.8% from data gathered in March. It’s predicted to strike the Southern Hemisphere of the moon’s near-side. That means it will be visible from Earth in telescopes. However, exactly where it will strike remains uncertain until the asteroid becomes visible again in 2028 when its orbit next brings it relatively close to Earth. The authors recommend a planetary defense mission to change the orbit of YR4.
Danger On The Moon
Although satellites would be threatened, the biggest dangers lie on the moon and in its orbit. An asteroid strike would cause ejecta to impact a wide area of the lunar surface, potentially threatening astronauts or a potential lunar base.
Spacecraft operating on the moon would also be in danger. They currently include NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, while NASA’s planned Lunar Gateway could be in orbit by 2032. On Wednesday, Firefly Aerospace announced plans to launch a new lunar imaging service called Ocula using its Elytra spacecraft, ostensibly to help commercial companies identify mineral deposits on the moon’s surface and map future landing sites.
Yr4’s ‘spectacular’ Meteor Shower
About 10% of the ejecta produced by the asteroid striking the moon would be propelled into space, potentially causing a meteor shower that “could last a few days and be spectacular, though the number of visible meteors somewhat muted by the low entry speed of ejecta,” reads the paper.
Any YR4 meteor shower would come just eight days after the peak of the Geminids, one of the very few annual displays caused by debris from an asteroid rather than a comet. Peaking on December 13-14 each year when up to 12 “shooting stars” can be seen, the Geminids are the result of asteroid 3200 Phaethon, which orbits the sun every 1.4 Earth years.
Further Reading