Birds, by design, tend to be small, light and streamlined. Yet there are some that push the … More
Birds of prey are defined by their sharp talons, hooked beaks, keen eyesight, and carnivorous diet – all of which enable them to hunt, kill or scavenge other animals for food.
The bald eagle is a classic example of a bird of prey. It has a powerful, hooked beak. It has sharp talons for catching fish. Its eyesight is incredible. And it has a carnivorous diet, mainly eating fish and small mammals.
An example of a bird that wouldn’t qualify as a bird of prey is the American robin. The robin is much smaller and has a diet consisting mainly of worms, berries and insects. It doesn’t have talons and its eyesight isn’t nearly as impressive as a bald eagle’s.
There are several hundred birds of prey that exist in the world today. Some belong to the family Accipitridae, which comprises hawks, eagles, kites and harriers. Others belong to the family Falconidae and are falcons. Owls, ospreys, vultures and the snake-hunting secretarybird also fall into the bird of prey category.
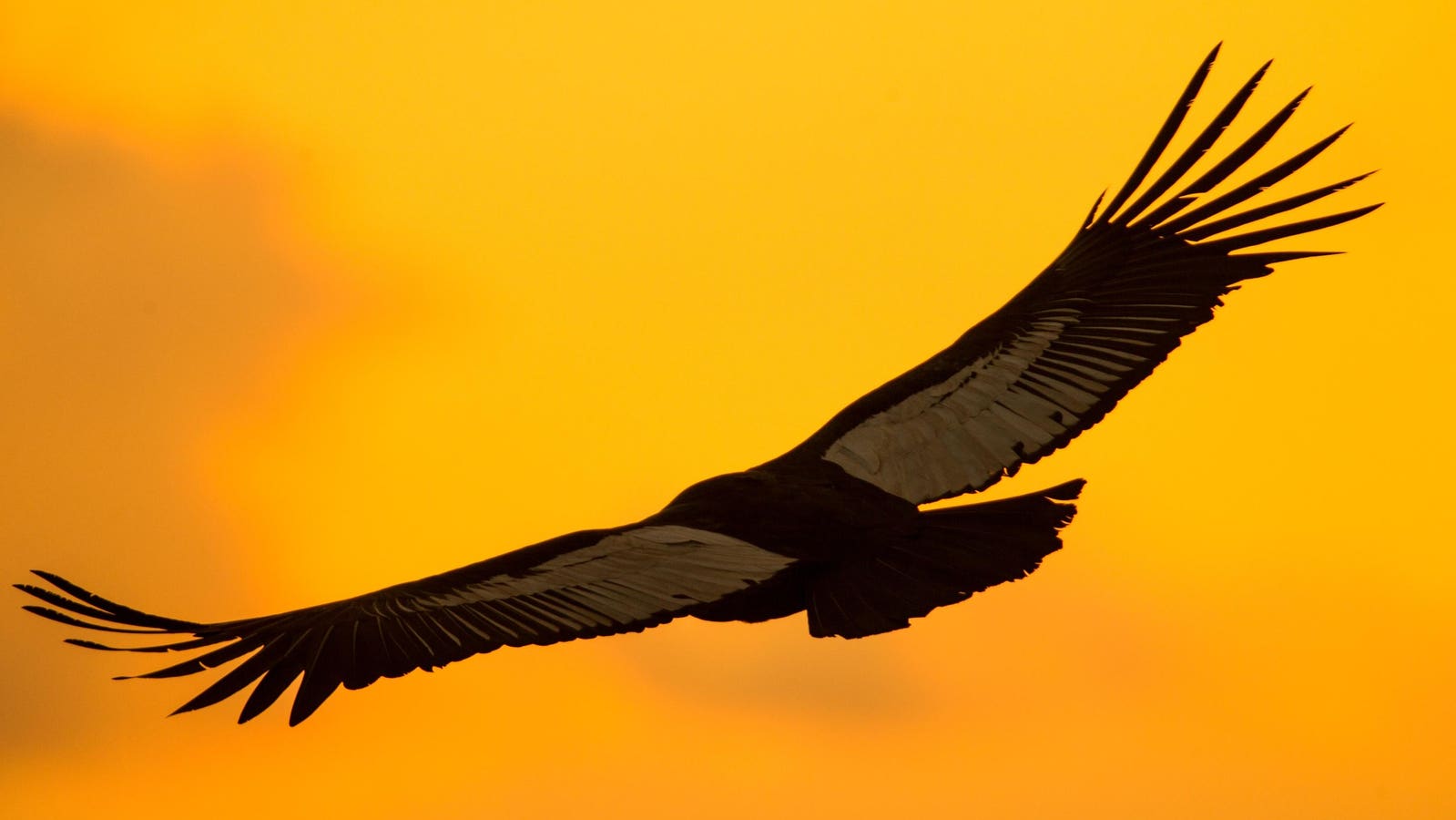
The largest bird of prey happens to be a vulture – a condor, to be precise. It is the Andean condor and it weighs up to 35 pounds. It is not the heaviest bird (that would be the flightless ostrich) and it is not the heaviest flying bird (that would be the great bustard) but it is the heaviest bird of prey. Here is the story of this fantastic flying creature.
The Andean Condor – A Superlative Among Superlatives
Andean condor perched on a rock, displaying its powerful build and characteristic bald head.
The Andean condor (Vultur gryphus) has a wingspan of 10+ feet (the largest wingspan of any land bird). Despite its 30+ pound physique, it soars effortlessly, gliding on thermal air currents with minimal wing-flapping. This is a skill that conserves energy during long flights.
Unlike many birds of prey that actively hunt, the Andean condor is primarily a scavenger. It feeds mainly on the remains of dead animals, often spotting carcasses from high in the sky due to its exceptional eyesight. This role is vital in its ecosystem, as condors help clean up dead matter, making sure none of nature’s bounty is wasted.
Its bald head, often tinted with red or yellow hues, is an evolutionary adaptation to its scavenging lifestyle, helping to keep the head clean when feeding on carcasses.
The condor’s size and soaring ability allow it to travel vast distances across the rugged Andean landscape in search of food. Its wings are broad and equipped with “primary feathers” that spread out like fingers, providing extra lift and maneuverability, which is crucial in navigating mountainous wind currents. Remarkably, these birds can fly for hours without landing, covering more than 150 miles in a single day without flapping their wings.
Sidebar: Impressed by the Andean condor? Meet the world’s tallest, and rarest, eagle here:
The Andean condor’s soaring ability has been quantified in extraordinary detail. A 2020 study published in PNAS used high-resolution biologging data to track every wingbeat of wild Andean condors across more than 200 hours of flight. The researchers found that condors flap their wings for less than 1% of their total flight time, with one bird covering over 100 miles in a single stretch without flapping at all.
Most of the energy expenditure is concentrated during takeoff, while the rest of their movement is powered almost entirely by rising air currents. Even immature birds with limited experience were able to navigate mountainous terrain for hours at a time without powered flight, highlighting the species’ extreme specialization for energy-efficient soaring. This efficiency is essential for aerial scavengers like the condor, since their large bodies make each wingbeat metabolically expensive.
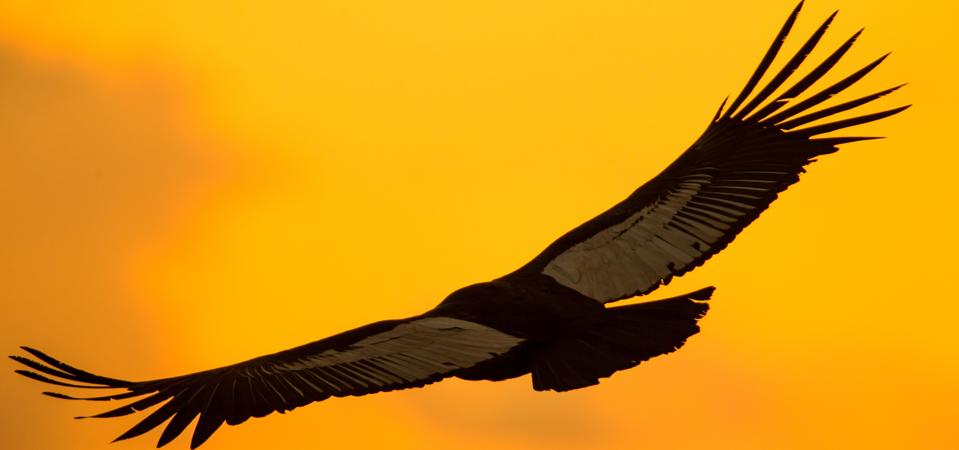
Andean condor soaring over the Andes, showcasing its massive wingspan and effortless gliding … More
Engineers have even recently looked to the Andean condor for inspiration in designing more efficient wind turbines. You can read this article for the full details, but here are the cliff notes: A 2024 study published in the journal Energy found that mimicking the shape of the condor’s wings led to a more efficient wind turbine blade, with an estimated 10 percent increase in energy production. Researchers added curved tips, known as winglets, to existing turbine blades. Modeled after the condor’s splayed wingtips, these modifications created a more aerodynamic design that reduced drag and increased lift.
The Andean condor is culturally important to the indigenous peoples of the Andes. It is looked to as a symbol of power, health and freedom, and features prominently in Andean mythology and folklore.
The Andean condor faces many conservation challenges. Habitat loss, poisoning from carcasses tainted with pesticides or lead, and hunting have led to declining populations in some areas. Conservation efforts, including captive breeding and habitat protection, are ongoing.
When comparing the Andean condor to other large birds, it holds a unique niche. While the ostrich dwarfs the Andean condor in weight, the ostrich is flightless. The great bustard, though sometimes larger than the Andean condor, is not nearly as capable a flyer. The condor, however, combines size with unparalleled soaring ability, making it the king of birds of prey.
Are you an animal lover who owns a pet, perhaps even a pet bird? Take the science-backed Pet Personality Test to know how well you know your little friend.