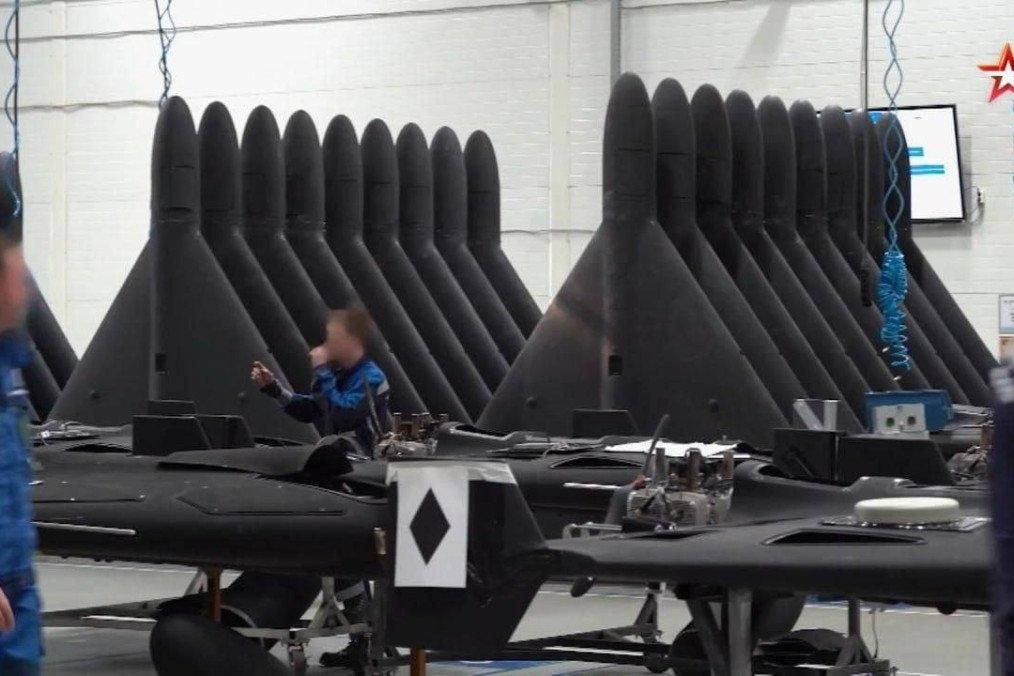
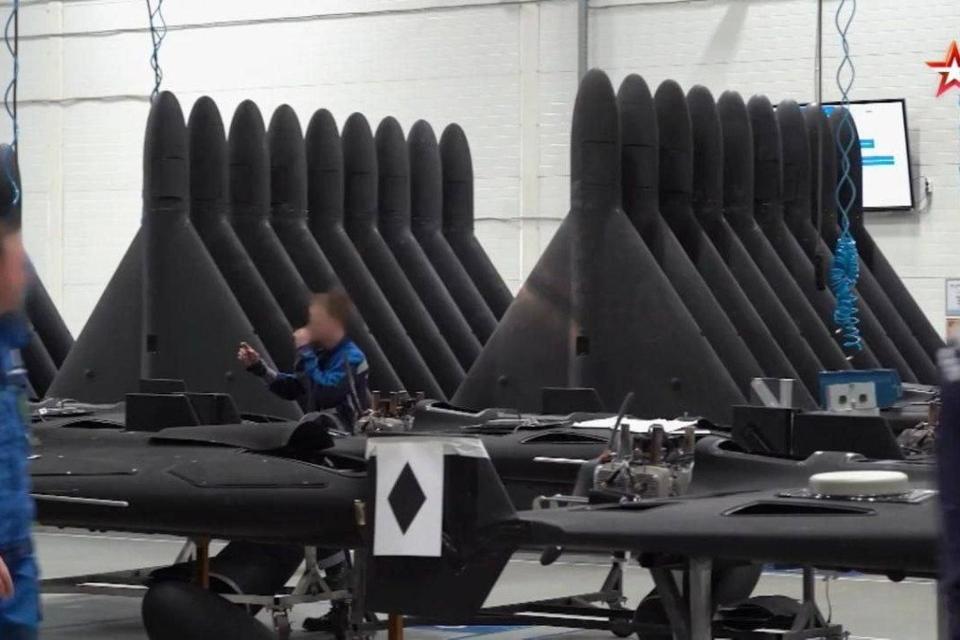
New footage shows mass production of Shahed drones at a Russian facility in Alabuga, Tartarstan
On July 20th,Russian state television showed new footage from the giant drone factory which makes Iranian-designed Shahed-136s, revealing the sheer scale of production. The facility in Alabuga a thousand miles East of Moscow has ramped up production roughly tenfold in the last year, enough for more than 700 attack drones to be launched in one night. That could rise to 2,000 Shaheds a night by the end of the year, according to Major General Christian Freuding of Germany’s Situation Center for Ukraine.
Now plans are afoot for the U.S. to launch drone barrages of its own, with the Pentagon unveiling a new type of weapon apparently in response to a presidential request. But is the Pentagon ready to compete with Russia in launching mass drone attacks?
Quantity Has A Quality Of Its Own
Tactical “Tomahawk” Block IV cruise missile,, the U.S. choice for precision long range attack.
Traditionally the U.S. military has favored sophisticated, highly capable weapons like the Tomahawk cruise missile. This is a 20-foot-long weapon flying under 300 feet to avoid radar at around 500 mph and, delivering a 1,000-pound warhead to targets around 1,000 miles away. It has led to attack in many recent operations, including strikes on the Houthis in Yemen earlier this year.
In the latest U.S. Navy budget, a batch of 40 Tomahawks cost $1.9 million each. That is not a lot of missiles in the arsenal, especially considering that many may not reach their targets. On 12th July, Russian launched 26 Kh-101 cruise missiles at Ukraine, along with a number of other missiles and hundreds of drones. 25 of those 26 missiles were shot down by air defenses.
The Shahed has a similar range and accuracy to the Tomahawk, but flies at a quarter of the speed and carries a tenth as much explosive. A high proportion of the drones were shot down in July 12th too – over 90% — but as these cost around $35k each they look like a much more cost-effective way of hitting a target. Especially if a 1,00-pound warhead is not needed.
President Trump remarked on the need for a U.S. equivalent of the Shahed at a Business Roundtable in Qatar in May, saying:
The new LUCAS attack drone
“We’re coming up with a new system of drones because drones are really … drones really seem to be taking over that war… I asked one of the companies, I said, I want a lot of drones and in the case of Iran, they make a good drone and they make them for $35,000, $40,000.
So I said to this company, I want to see. They came in two weeks later with a drone that cost $41 million. I said, that’s not what I’m talking about, $41 million. I’m talking about something for $35,000, $40,000, where you send thousands of them up and that’s a great way — and they’re very good too and fast and deadly, horrible, actually, when you look at what’s happening with Russia and Ukraine.” (My emphasis)
Part of this speech was quoted on a signboard in front of the new Low-Cost Uncrewed Combat Attack System (LUCAS) displayed in the Pentagon courtyard at an event attended by Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth last week.
LUCAS looks very much like a Shahed clone, and is billed as “designed to rival Iran’s widely used Shahed-136 loitering munition, in a push to expand affordable airpower options for modern battlefields.”
But the new drone may not be all that it seems.
A Weapon, Or Just A Target?
LUCAS is made by Arizona contractor SpektreWorks and LUCAS looks very much like a version of their FLM-136, a copy of the Shahed-136 made for ‘threat emulation’. In other words it was designed as an aerial target for U.S. forces to get realistic practice shooting down Shaheds.
Norma Jean Dougherty, aka Marilyn Monroe, assembling target drones in 1945
The U.S has been using target drones for decades. In WWII an Army photographer captured one Norma Jean Dougherty (later to become famous as Marilyn Monroe) on the assembly line for RadioPlane OQ-3 target drones. Generations of target drones followed, including the Teledyne Ryan Firebee, successfully converted into a reconnaissance drone in the Vietnam War.
It is obvious why the military would want a drone target representing a Shahed. The U.S. Navy came under attack from a variety of similar drones launched by the Houthis in the Red Sea recently and needs to practice the best ways to tackle them. However the requirement for a target drone is not the same as for an attack drone. The specifications of the FLM-136 show that while it is an excellent substitute for shooting practice, it does not have quite the performance the real thing.
U.S. LUCAS attack drone on display week
The FLM-136 has the same size and speed as the Shahed-136 but weighs about half as much as and carries half the payload. Its range of around 500 miles is less than half that of the Shahed.
What we do not know is the unit cost of the FLM-136, which is a key metric. It is possible that it really has been procured for the desired ‘$35,000, $40,000’ but this would be remarkably low by Pentagon standards. Previous small drones have been known to cost more than their weight in gold, and the BQM-167 Skeeter, the Air Force’s reusable jet-powered drone, costs $1.7 million each.
Presumably the LUCAS is at least less than ‘$41 million,’ or a Tomahawk cruise missile. But without seeing numbers we cannot know for sure.
Return To The Age Of The Jet Bomb
A series of images showing the trajectory of a JB-2 buzz bomb during take off in the desert, USA, … More
Back in WWII, the U.S. was big on the idea of reverse-engineering enemy weapons and producing them at scale. The Republic-Ford JB-2 ‘Loon’ was a direct copy of the German V-1 ‘Doodlebug’ which carried out the same roles as the Shahed does now. ‘JB’ was short for ‘Jet Bomb’. V-1s had caused tremendous damage in Europe. The plan was to use JB-2s to bombard Japan into submission with thousands of JB-2s with no risk of losing aircraft, launching them from the decks of aircraft carriers from where they could hit any part of Japanese territory.
The military initially ordered 1,000 JB-2, with the same number to be made each month. The project was canceled when Japan surrendered while the first weapons were still on their way to the Pacific.
Palmer Luckey, founder of Anduril, has said that he wants to see a return to the mass-production approach of WWII and “bring mass to the fight.” This means vast numbers of Anduril’s low-cost Barracuda cruise missile/drones and other weapons rather than a handful of Tomahawks. But Anduril products were not apparent at the Pentagon event.
Whether the Pentagon is serious about this approach, or whether they just wanted to show the Secretary of Defence that the U.S. could make something that looks like the Shaheds the President asked for, is another matter.
Meanwhile Ukraine is producing its own low-cost, long-range attack drones and plans to hit Rusia with 30,000 this year. These include a mix of sophisticated types and ultra-low-cost designs with bodies fashioned from plastic pipe. The drone arms race is well under way, and the U.S. is starting from behind.